We know that our lifestyle affects our health. We've heard it a million times before. Some of us take it more seriously than others. What we haven't really heard much of is how this relates to the inherited illnesses that people are at-risk of getting. Interestingly, again, it is actually lifestyle that significantly affects our chance of actually getting the illness that we're at risk of. For instance, someone born with a BRCA mutation, isn't necessarily going to get breast cancer. They are more at risk of...
Detecting the rare, renegade cancer cells
Very early in tumour development, the tumour may send out some extremely sneaky cells into the bloodstream. The cells may circulate in the bloodstream as dormant cancer cells for months or years, and may even survive cancer treatment aimed at treating a primary cancer. The cells are called Circulating Tumour Cells, and are the cause of cancer spread, metastases. It is the metastases, rather than the primary tumour, which is most often responsible for patient fatality. Circulating Tumour Cells have become a hot topic in...
Gene expression and the regulation of genes
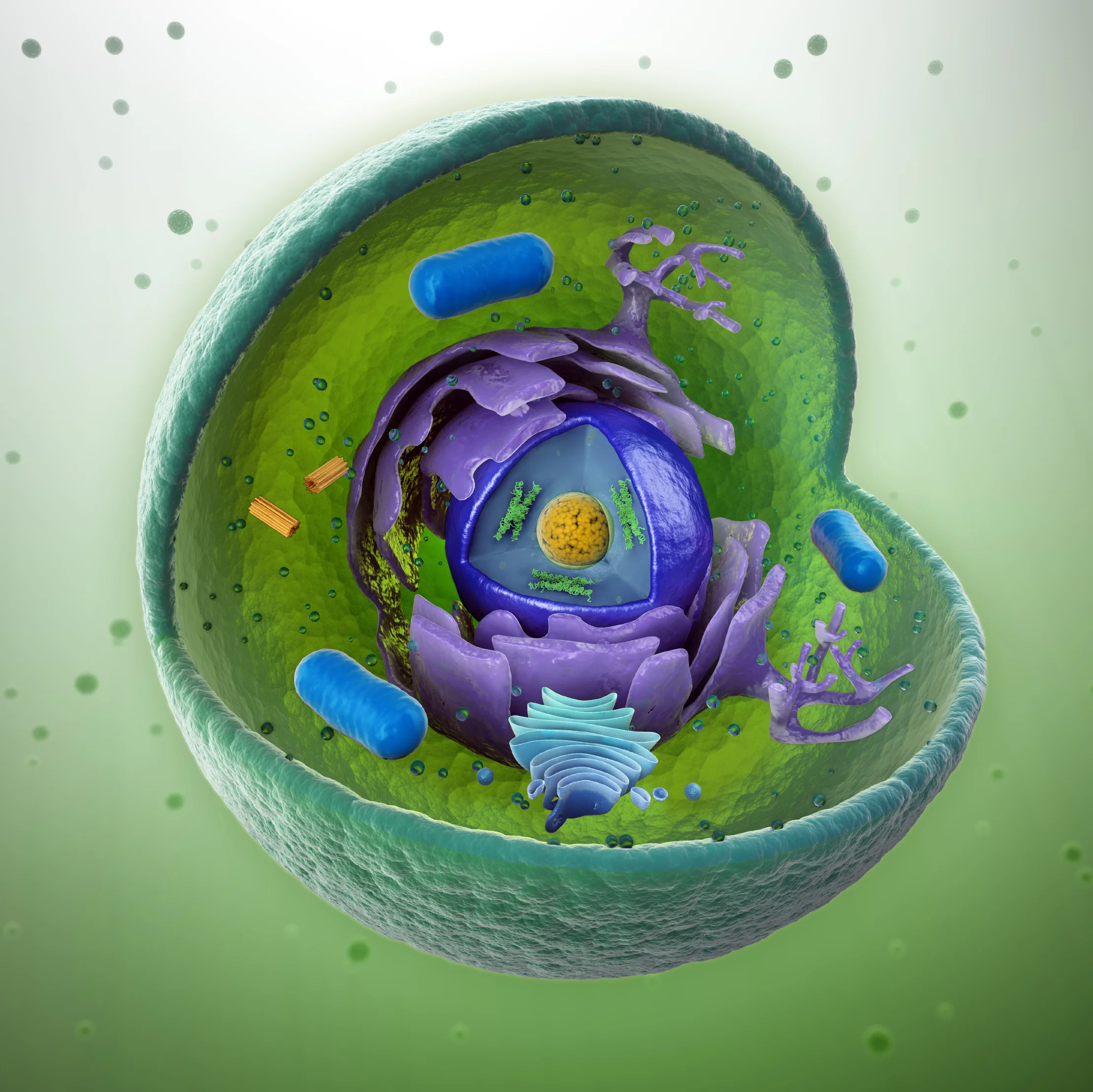
A gene that is expressed, simply means that it is active. If a gene is a set of instructions, gene expression simply means that the instructions are being read and acted upon by cellular machinery. The result of gene expression is a functional protein, or phenotype.
The cellular machine that 'reads' the...
Genetics, explained
What is DNA? What is a gene? What is a mutation?
In brief, DNA is a long molecule that stores information. DNA is located in the centre (nucleus) of every cell and contains all the instructions necessary for the organism to function. Similar to pearls on a necklace, along the DNA strand there are millions of basic structural units called nucleotides. Each nucleotide (pearl) is one of four types: A, T, G or C, as determined by the nitrogenous base they contain, i.e., nucleotide 'A' has Adenine, 'T' has Tyrosine, 'C' has Cysteine and 'G' has Guanine. These four types of...
What is a biomarker and how are CTCs defined as both a biomarker and as a carrier of biomarkers?
A biomarker is a short way of saying 'biological marker.' By definition, biomarkers are biological indicators of the existence of either a physiological (normal) or pathogenic (disease) process, or pharmacological response. Biomarkers include things like cells and proteins, and/or specific sequences of DNA, mRNA transcripts, non-coding RNAs.
Circulating Tumour Cells - tell me more
From the time malignant tumours have reached a size of two milimetres, they release thousands of malignant cells into the circulation. Most of these cells die or get kiled off. The more aggressive ones survive and remain in the bloodstream as 'Circulating Tumour Cells,' abbreviated as CTCs. These cells have the potential to...